|
||
|
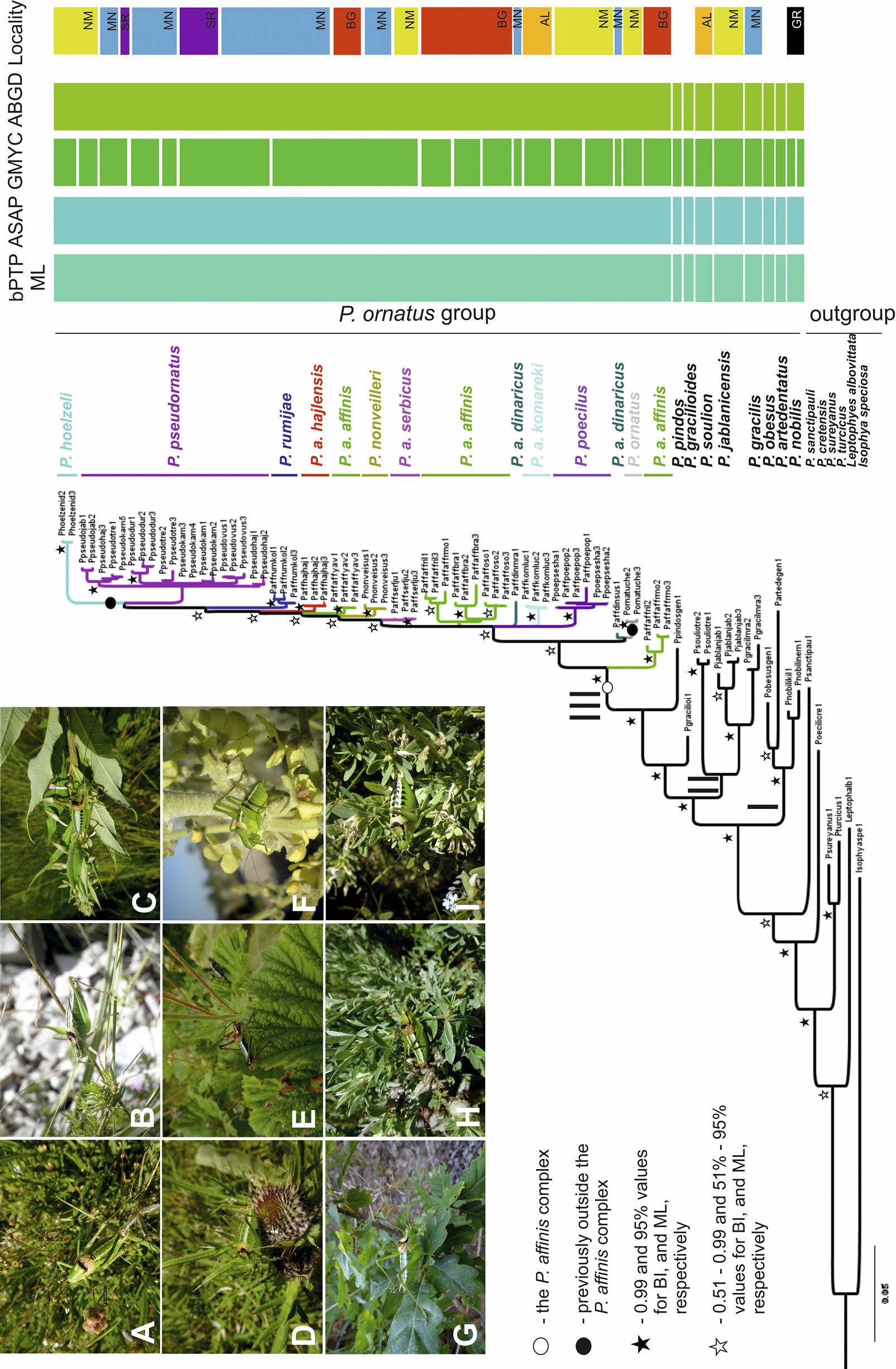
A Poecilimon pseudornatus, B P. gracilioides, C P. a. affinis, D P. a. hajlensis, E P. gracilis, F P. nobilis, G P. rumijae, H P. hoelzeli, I P. ornatus. Photos: Dragan Chobanov. Bayesian inference tree from a dataset including COI, ND2, CR, and ITS1 sequences of the Poecilimon ornatus group. Bayesian (BI) and Maximum likelihood (ML) topologies were consistent, so only one tree is shown. I – the first clade, II – the second clade, III – the third clade. The right panel shows groupings from different species delimitation approaches, as follows: bPTP ML – the Poisson Tree Processes; ASAP – Assemble Species by Automatic Partitioning; GMYC – maximum-likelihood approach based on the general mixed Yule-coalescent model; ABGD – Automatic Barcode Gap Discovery. The last grouping is based on localities of the taxa studied (NM – North Macedonia, MN – Montenegro, SR – Serbia, BG – Bulgaria, AL – Albania, GR – Greece). Scale bar: number of substitutions per nucleotide position. |